History, Location & Origin | Lepidolite
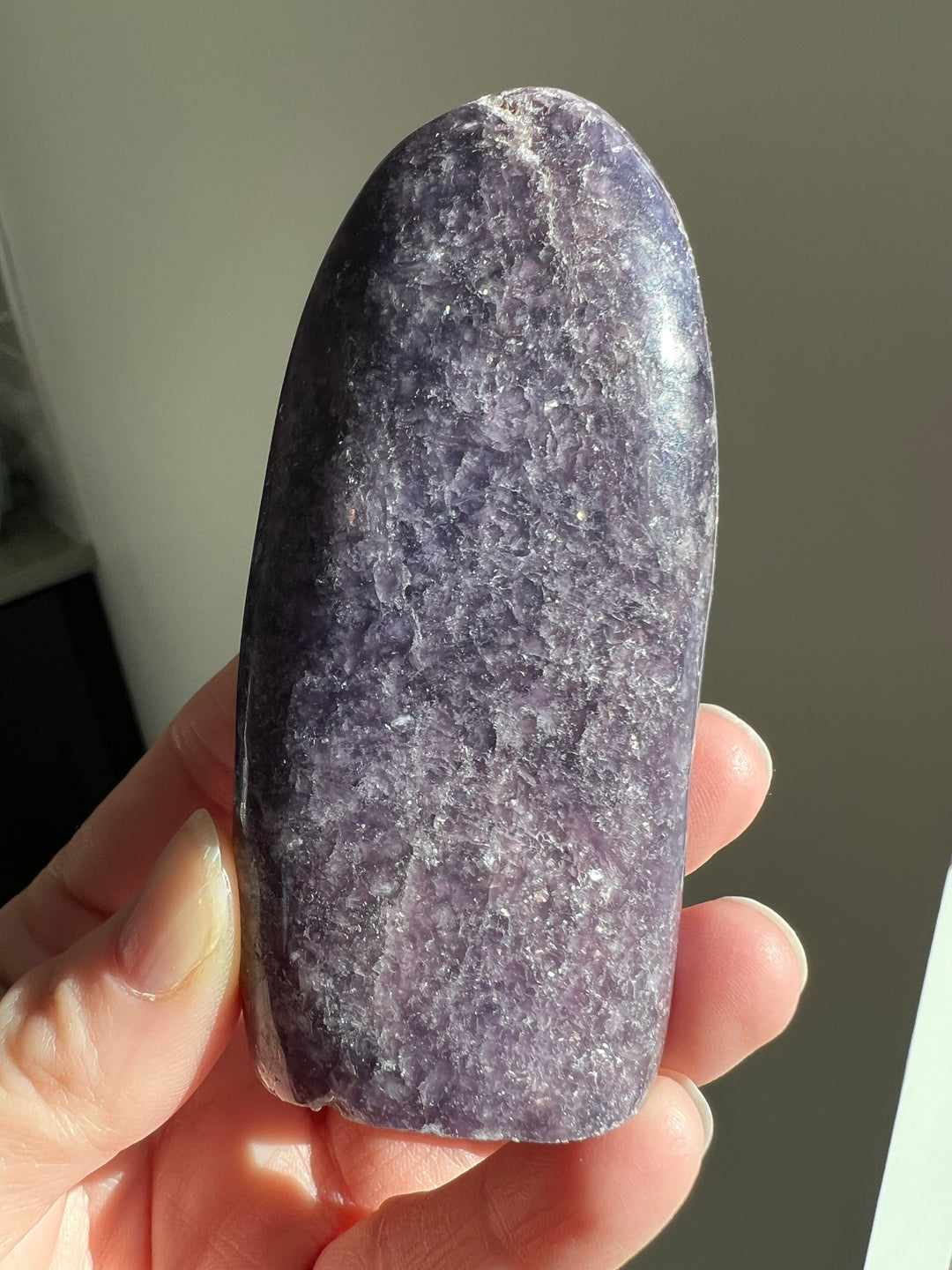
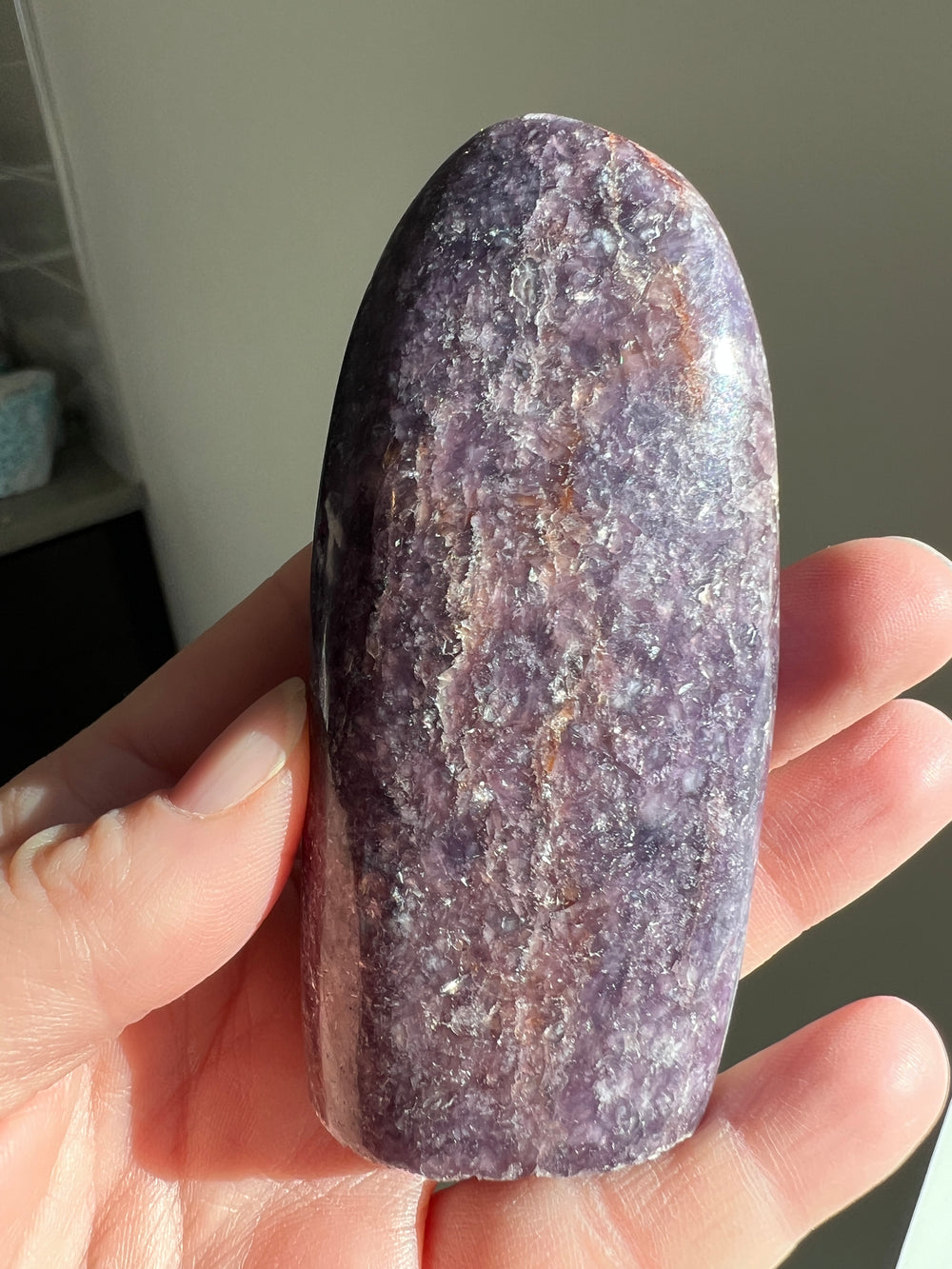
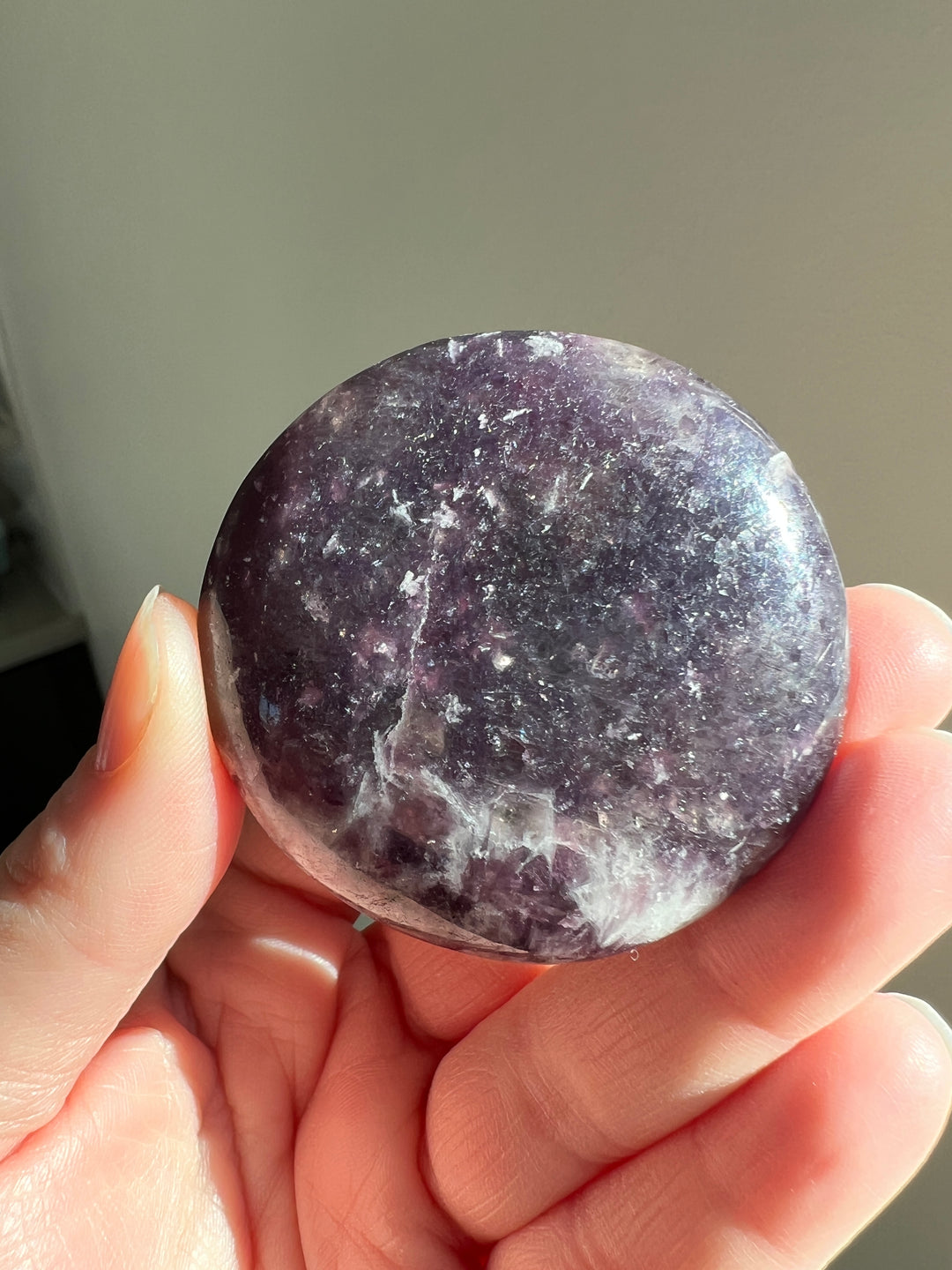
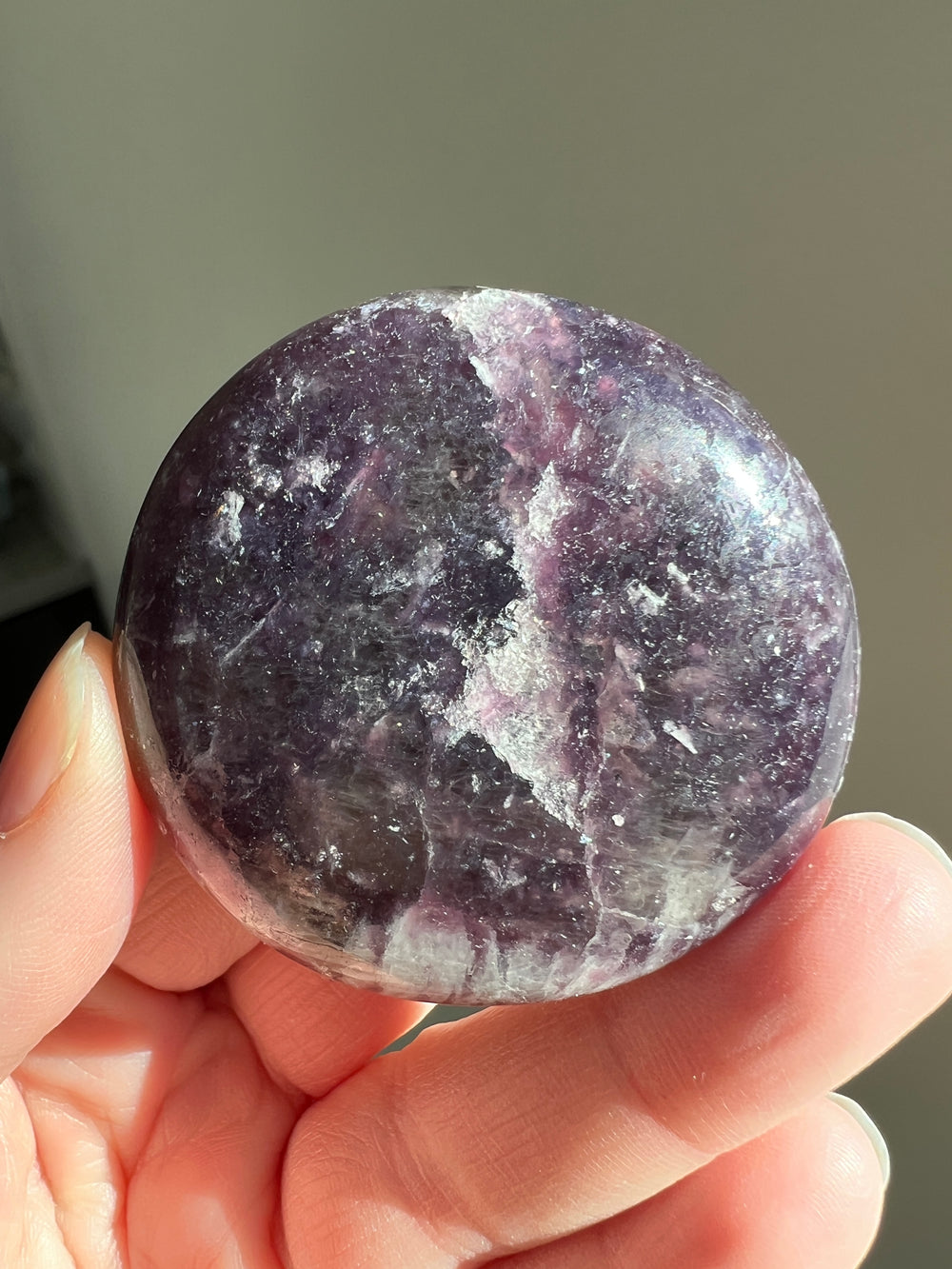
Lepidolite, a lilac-gray or rose-colored member of the mica group, is a mineral largely comprised of lithium, aluminum, and potassium. While not as historically prominent as some other minerals, Lepidolite has a notable background in both its geological significance and its more recent industrial and metaphysical uses.
Geological Formation and Composition:
- Lithium Source: Lepidolite is one of the richest sources of lithium, which is a vital component in many modern technologies. The mineral typically forms in granitic masses and pegmatite dikes.
- Discovery: It was first described in the 18th century and was initially called "lilalite" due to its lavender color.
Geographical Locations:
- Primary Sources: Significant deposits of Lepidolite are found in Brazil, the Czech Republic, United States (California), Madagascar, and Canada.
- Mining: The extraction of Lepidolite is often associated with the mining of other lithium-bearing minerals.
Historical and Industrial Context:
- Industrial Use: The discovery of Lepidolite as a lithium source has made it important in industrial applications, particularly in the production of batteries and other electronic components.
- Scientific Interest: Its high lithium content also makes Lepidolite an object of study in geology and mineralogy.
Contemporary Significance:
- Gemstone and Ornamental Use: In recent times, Lepidolite has gained popularity as a gemstone and ornamental stone. It is often used in jewelry and decorative items due to its attractive color and shimmering quality.
- Metaphysical Properties: In metaphysical circles, Lepidolite is believed to have calming and stress-relieving properties. It is often used in crystal healing, though these claims are not supported by scientific evidence.
In summary, Lepidolite's significance lies in its lithium content which makes it industrially important, especially in contemporary technologies. Its aesthetic appeal as a gemstone and its purported metaphysical properties also contribute to its modern popularity.