Geological & Scientific Properties | Moldavite
Moldavite is a type of natural glass, technically classified as a tektite, known for its unique green color and formation history. Tektites are a form of natural glass created from the intense heat and pressure of meteorite impacts. Here's an overview of Moldavite's geological and scientific properties:
Chemical Composition and Structure:
- Composition: Moldavite is primarily silicon dioxide (SiO₂), similar to other forms of glass, but with impurities that give it a distinctive green color. It contains other oxides such as aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) and iron oxide (FeO).
- Formation: It was formed about 15 million years ago during the impact of a large meteorite in what is now the Ries crater in southern Germany. The heat and pressure from the impact fused the surrounding rocks and ejected the material into the atmosphere, where it cooled and fell back to the earth's surface.
Physical Properties:
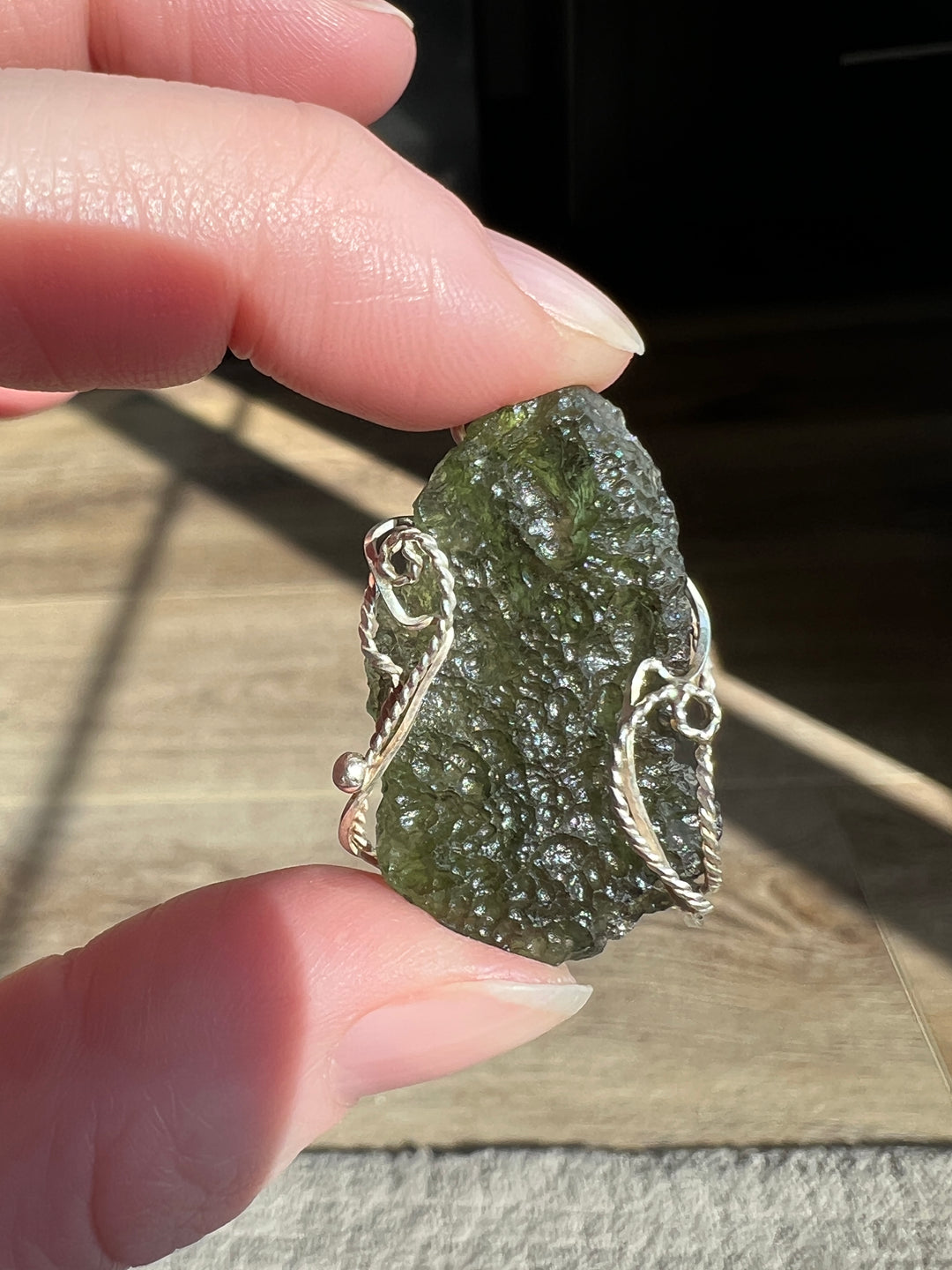
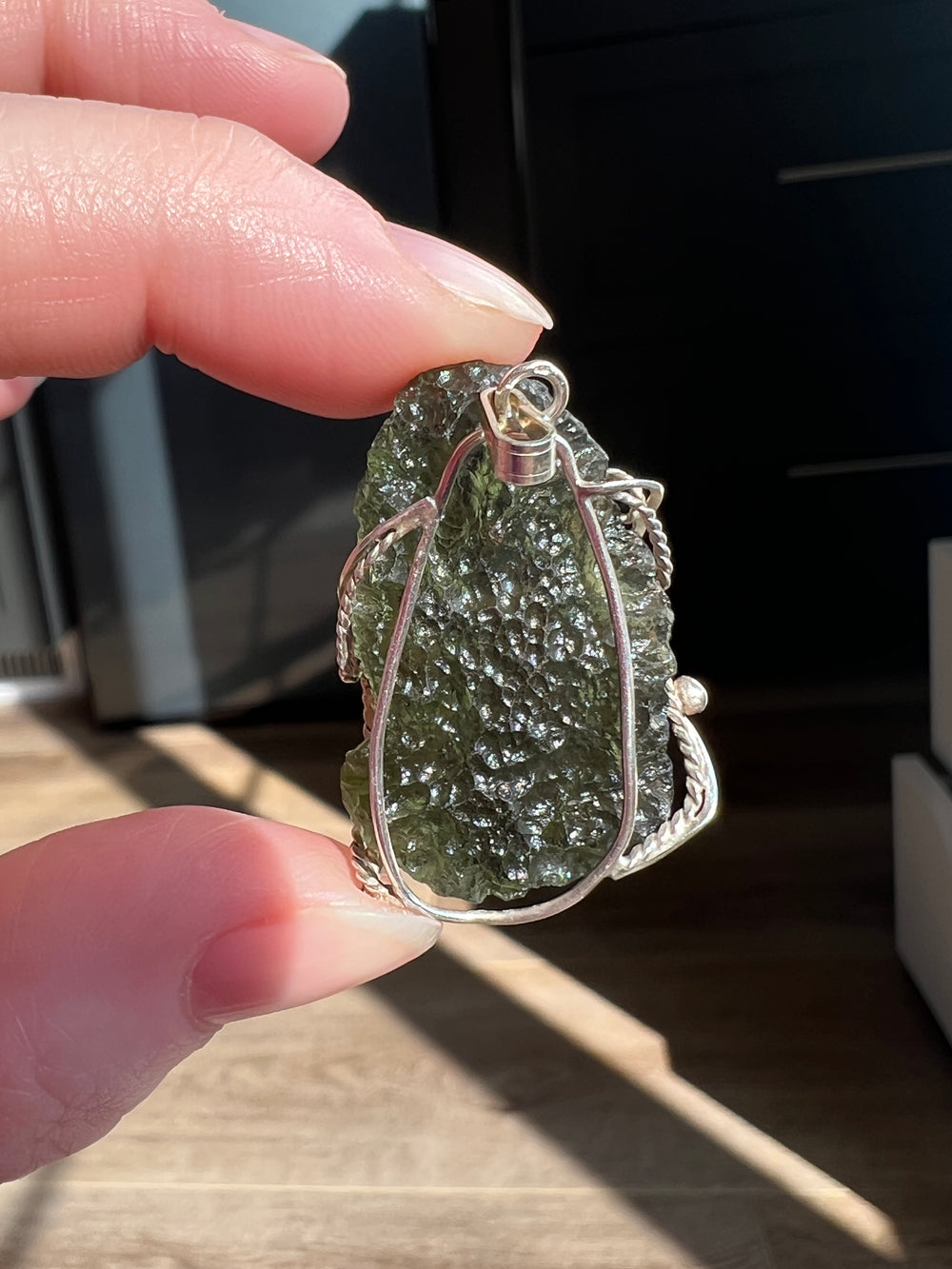
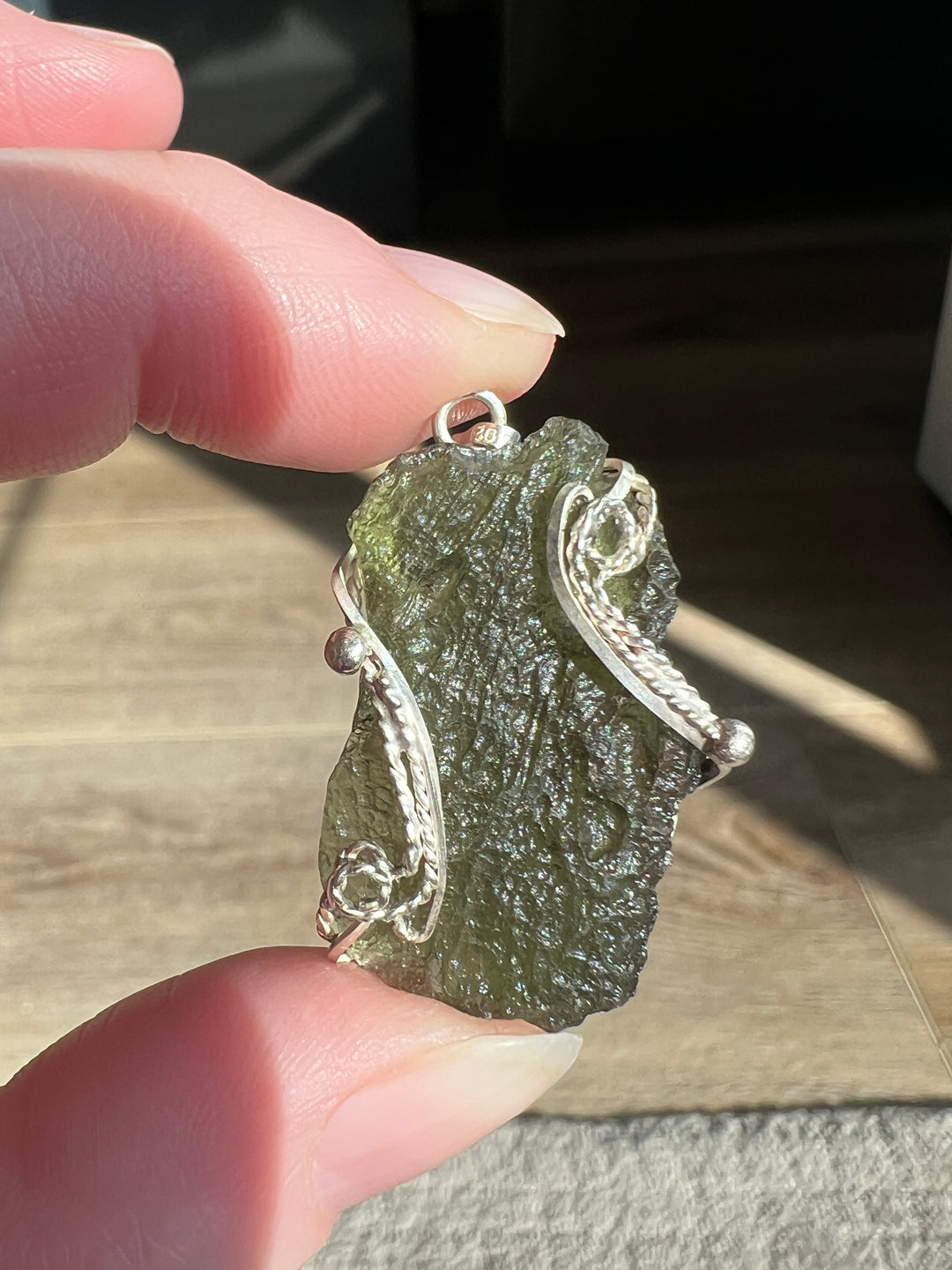
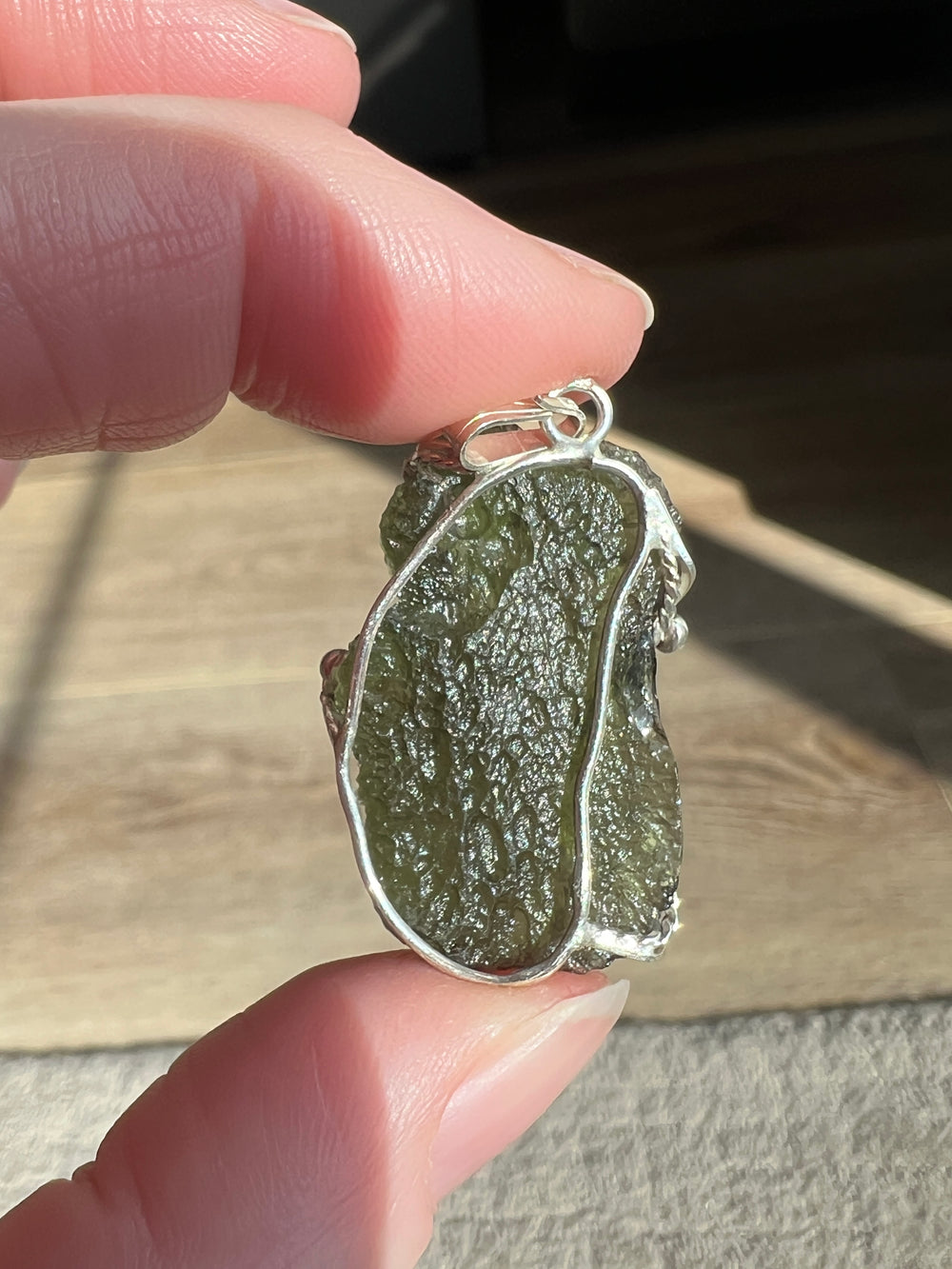
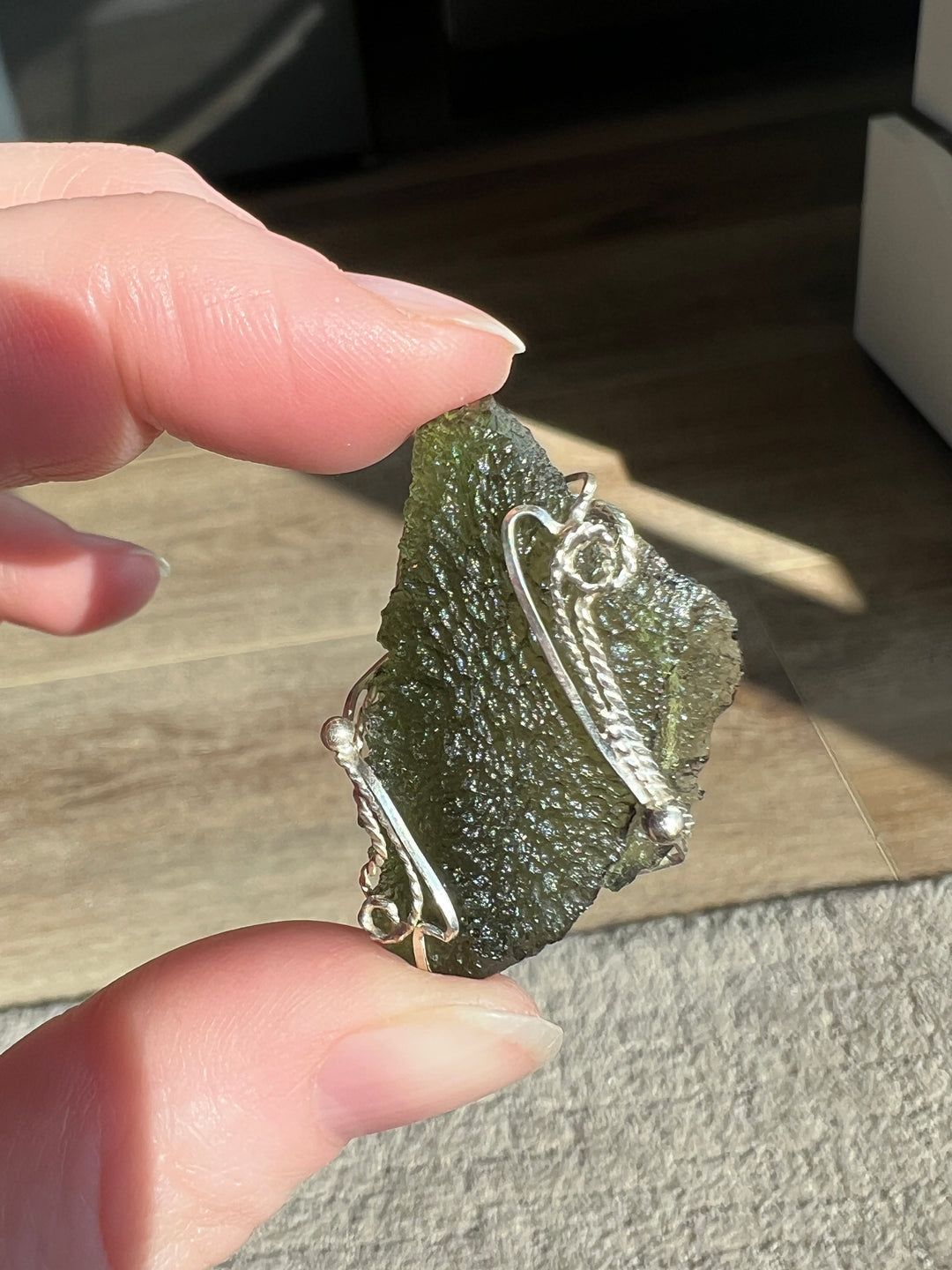
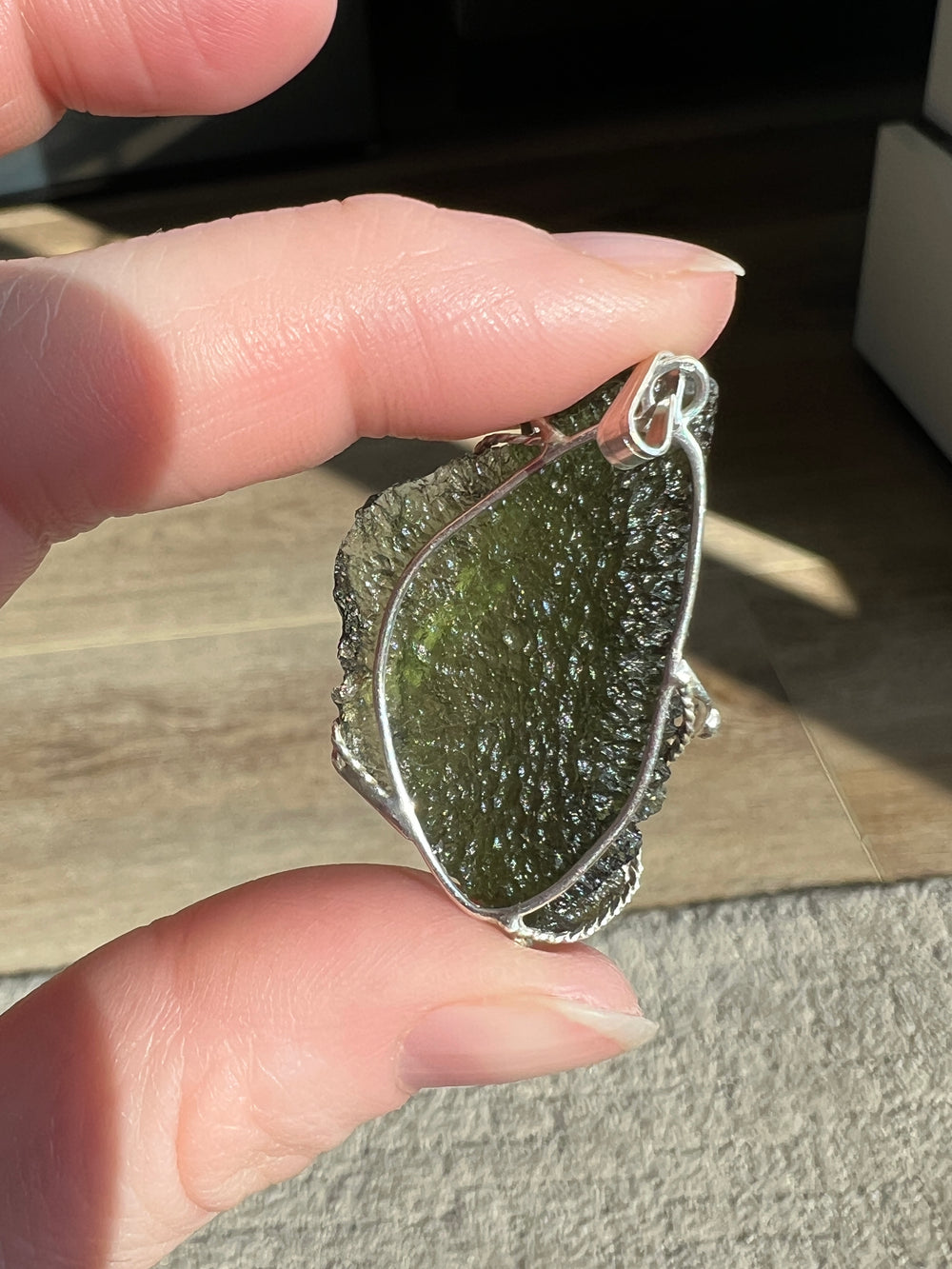
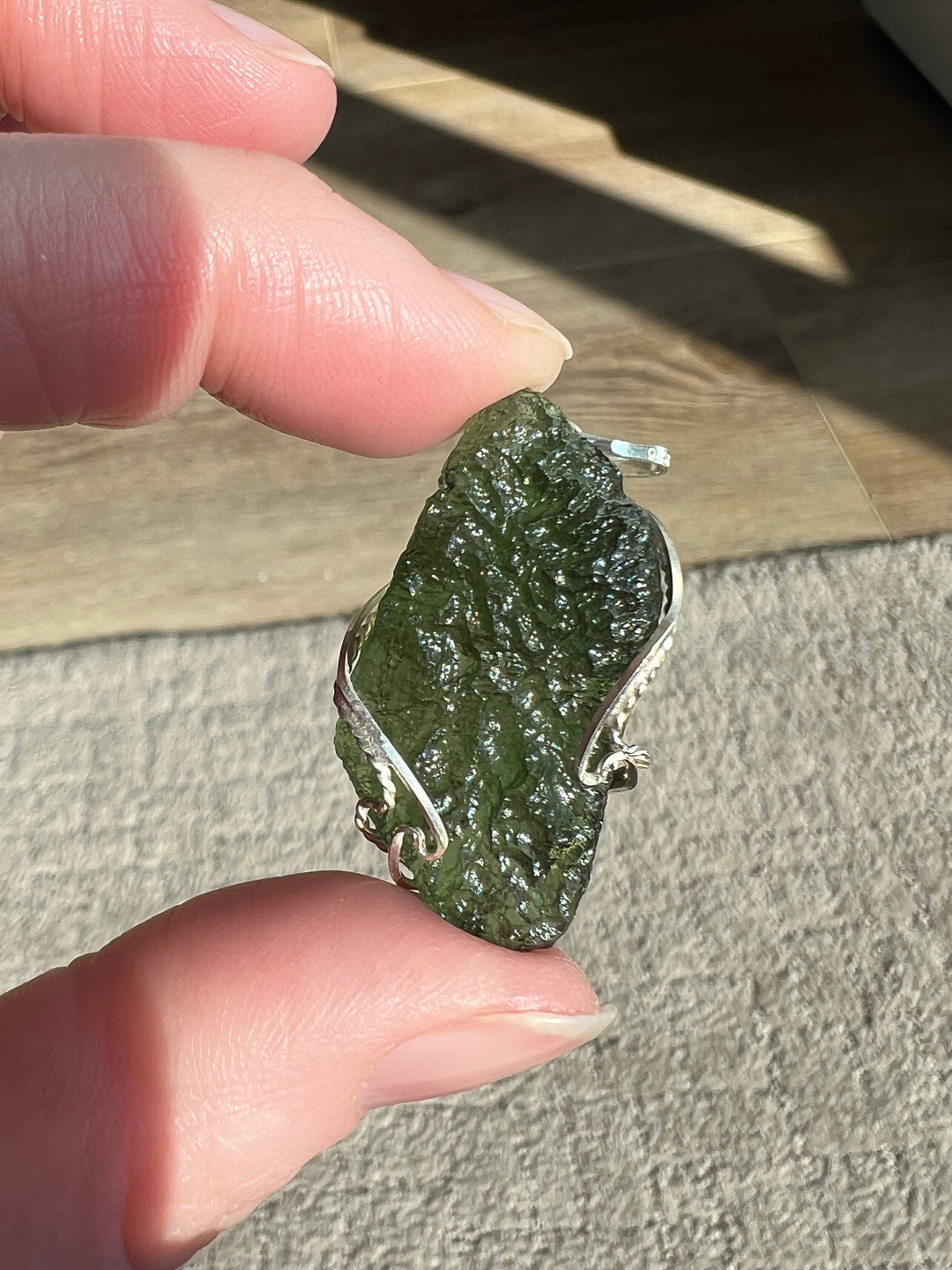
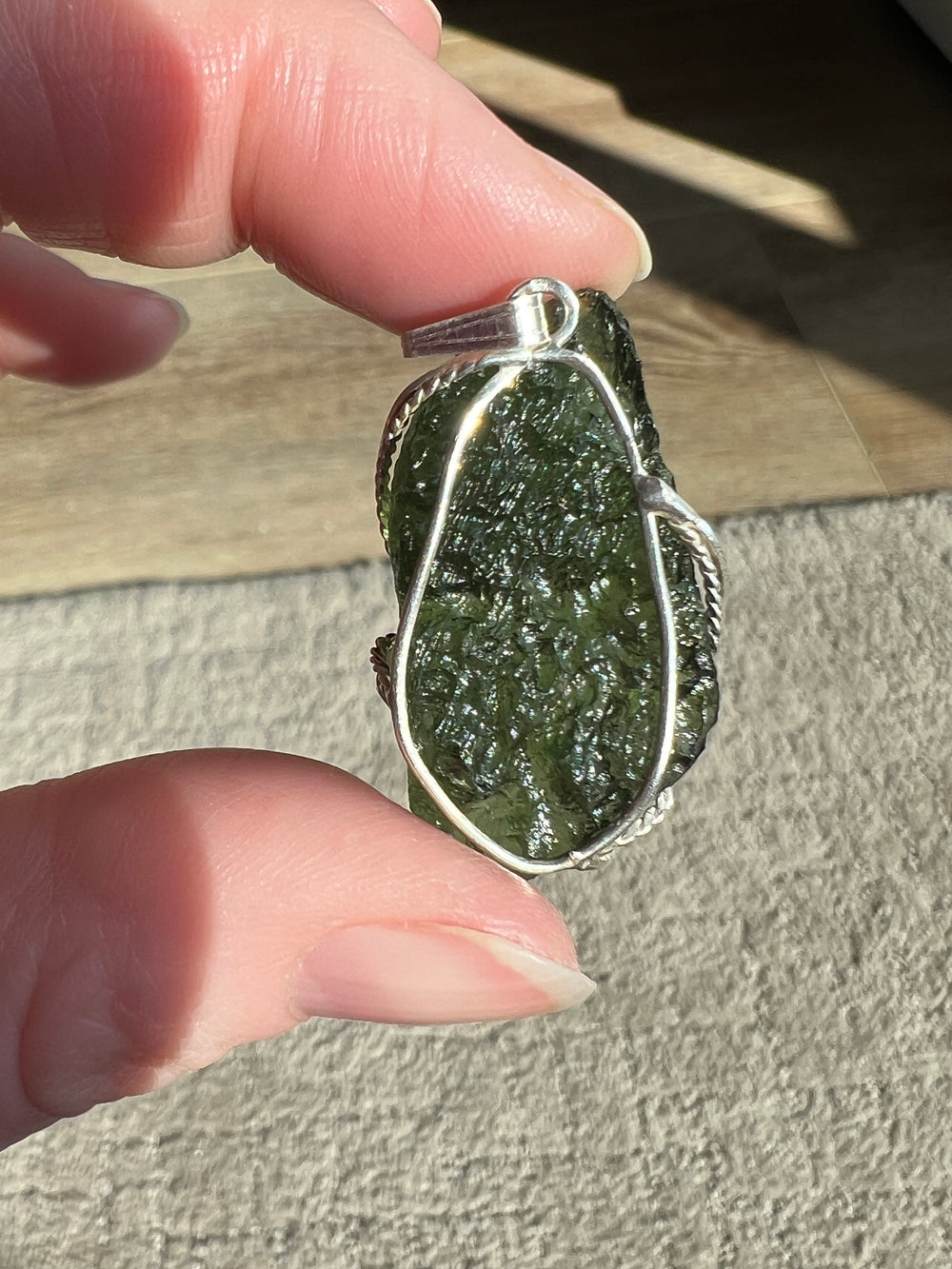
- Color: Moldavite is known for its olive to forest green color, which can be translucent to transparent.
- Hardness: It has a Mohs hardness rating of about 5.5, making it relatively soft compared to crystalline gemstones.
- Luster: Moldavite has a vitreous to dull luster.
- Transparency: This material ranges from transparent to translucent.
- Texture: It often has a distinctively pitted or wrinkled texture.
Geographical Occurrence:
- Locations: Genuine Moldavite is found only in the Moldau River valley in the Czech Republic and in some areas of Germany and Austria. This limited geographic distribution makes it relatively rare.
Moldavite is prized in both gemological and metaphysical circles. In gemology, its unique color and extraterrestrial origin make it a popular choice for jewelry, despite its relative softness. In metaphysical practices, Moldavite is often associated with transformative powers and is used in crystal healing, though these claims lack scientific basis. Its formation story, tying it to one of the earth's ancient meteorite impacts, adds to its allure and makes it a fascinating subject of study for geologists and collectors alike.